Distal Clavicle Resection (Mumford Procedure)
An arthroscopic procedure performed to relieve symptoms caused by arthritis of the acromioclavicular (AC) joint. Through 2 or 3 small incisions around the shoulder soft tissue in the AC joint is removed. The tip of the clavicle (collar bone) is then shaved down a few millimeters to create joint space. This in turn will reduce pain associated with arthritis. The Mumford procedure is frequently performed in conjunction with a subacromial decompression.
Contents
Common Questions About Distal Clavicle Resection (mumford Procedure)
Why do a distal clavicle excision?
A distal clavicle excision is performed when arthritis of the AC joint is severe. Most typically AC joint arthritis is from weightlifting, also known as “weightlifter’s shoulder”. When nonsurgical treatment such as physical therapy, anti-inflammatory medications, or cortisone injections have failed, then surgical treatment is offered.
What is a distal clavicle excision?
A distal clavicle excision is when the tip of the clavicle is burred down to widen the AC joint from arthritis. Typically the AC joint moves and does not make contact but when osteoarthritis is severe there is excessive contact between the acromion and clavicle. Bone spurs develop and this can become chronically painful.
How painful is a Mumford procedure?
The Mumford procedure or distal clavicle excision is done arthroscopically as opposed to in an open fashion. The ends of the bones that have been widened take 8 weeks to fully seal. During that period the shoulder is known to be sore but the patient has no motion restrictions after the procedure.
Distal Clavicle Resection (Mumford Procedure) Outcomes
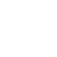
Preoperative MRI of patient clavicle to receive Distal Clavicle Resection (Mumford Procedure)
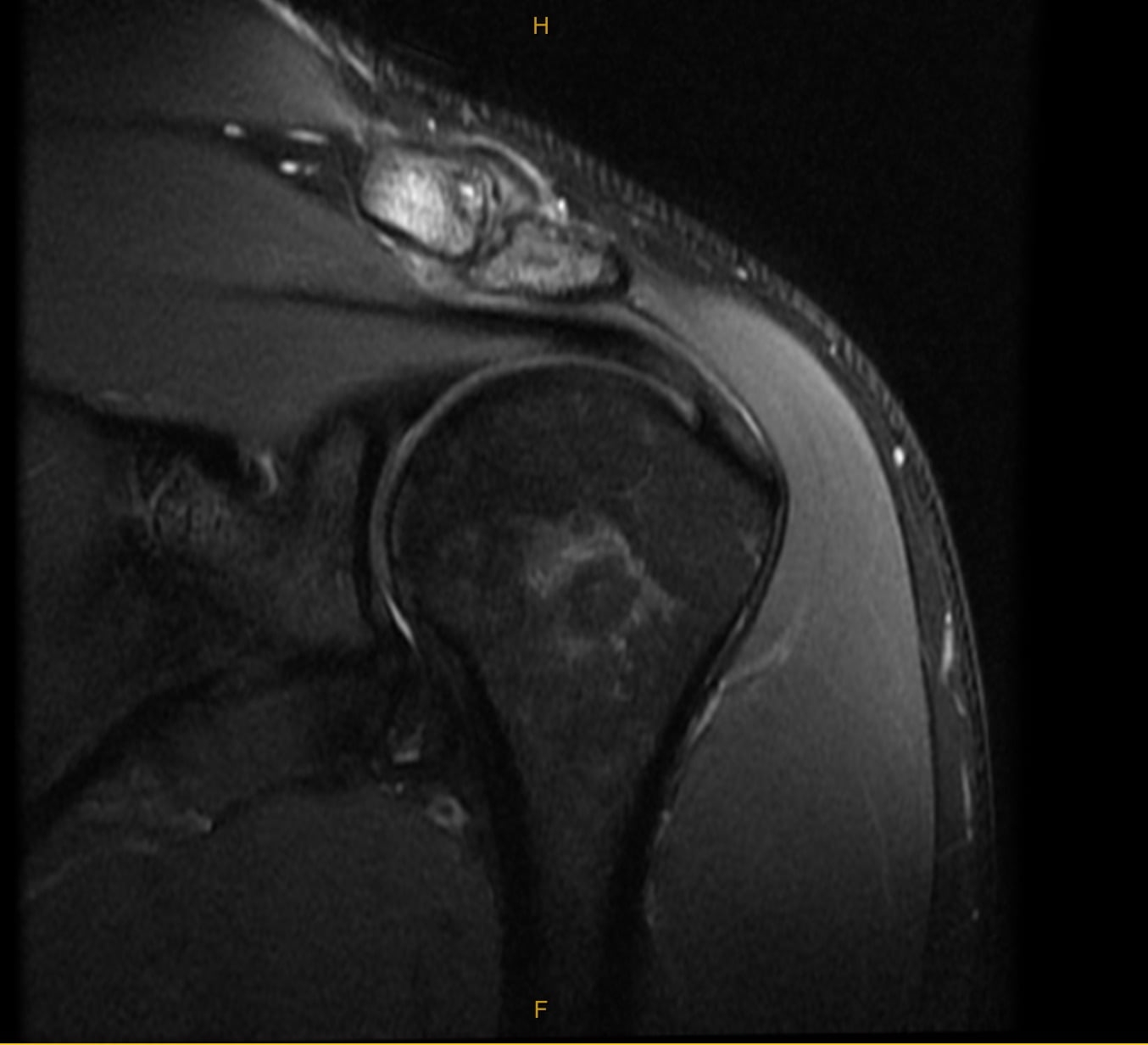
Post-Operative X-RAY of patient clavicle
Surgical Technique Video
The video below is age-restricted. You may need to log in to Youtube in order to view this video.