Tibia Fracture Repair
A surgical procedure performed to repair a broken tibia bone. The location of the break will determine whether the repair is done with a plate and screws or a rod introduced into the bone canal (intramedullary nail).
Contents
Plate and screw fixation: An incision is made to expose the broken bone. The bone fragments are then brought into alignment and fit with a metal plate and screws to keep them stable while they heal together.
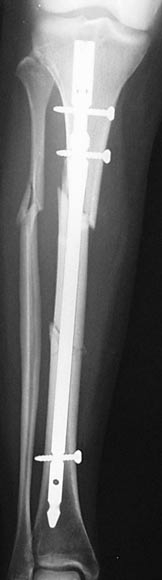
Intramedullary nailing: An incision is made to access the end of the bone. A hole is drilled through the bone to the medullary canal. The bone is brought into alignment and a metal rod is placed in the canal. The rod is secured with screws placed under X-ray guidance.A surgical procedure performed to repair fractures of one or both bones of the forearm. An incision is made to expose the broken bone. An additional incision is made if both bones need to be repaired. The bone fragments are then brought into alignment and fit with a metal plate and screws to keep them stable while they heal together.
Second Opinion by Dr. Chen on Yahoo! Fantasy Football Live
Common Questions About Tibia Fracture Repair
How long does it take for a tibia fracture to heal?
Most tibia fractures take at least 8 to 12 weeks to heal.
What is the difference between plate and screw fixation and intramedullary nailing?
Plate and screw fixation involves aligning the fractured bone and stabilizing them with a metal plate and screws. Intramedullary nailing involves drilling a hole into the bone and inserting a metal rod into the medullary canal. Both procedures use x-rays to confirm proper hardware placement.
What are intramedullary nails made of?
In most cases, intramedullary nails are created from titanium.
When is plate and screw fixation used?
Plate and screw fixation is used when intramedullary nailing is not an option. Examples include fractures that involve the knee or ankle joint. Plate and screw fixation is also preferable in children as intramedullary nailing can impact growth plates.
Example X-ray Images
Segmental Tibial Shaft Fracture
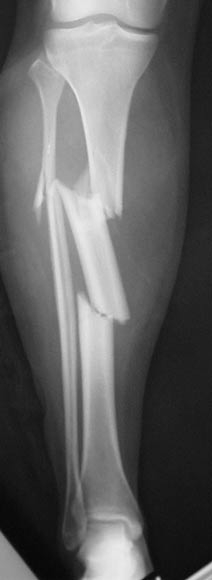
Repair of Tibial Shaft Fracture with Intramedullary Nail